Data Privacy and Security Risks in the ABC system:Full Guide
Data Privacy and Security Risks in the ABC ID system are critical concerns as education becomes increasingly digital. While the ABC system offers greater flexibility for students in Redeeming and Reversing Credits across institutions, it also exposes sensitive student data to potential threats.
This article examines the risks associated with the ABC system, highlighting the importance of safeguarding student information in this digital era, and suggests practical solutions to enhance data protection and security.

Centralized Data Storage: A Double-Edged Sword
Risk: Centralized databases offer an efficient way to store and access vast amounts of student data, but they also pose a significant Data Privacy and Security Risk. In the event of a data breach, a large volume of sensitive information can be compromised, affecting thousands of students.
Mitigation: To minimize this risk, educational institutions should implement robust encryption methods, both for data at rest and during transit. Additionally, access controls and role-based permissions should be enforced to restrict unauthorized access.
Inadequate Authentication Mechanisms
Risk: Simple passwords or inadequate authentication methods make the ABC system vulnerable to unauthorized access, increasing the likelihood of identity theft or data breaches.
Mitigation: Institutions must enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users, including students, staff, and administrators. This adds layer of security by requiring verification through multiple methods, such as passwords and biometric data or one-time passcodes.
Data Transmission Vulnerabilities And Security Risks
Risk: The transmission of sensitive data over unsecured networks exposes it to potential interception by cybercriminals, putting student records at risk.
Mitigation: To address Data Privacy and Security Risks and ensure secure data transmission, institutions should implement Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption and rely on Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for all internal and external communications. These measures prevent unauthorized third parties from intercepting and accessing confidential data.
Insider Threats: The Hidden Danger
Risk: Insider threats remain one of the most insidious risks to the ABC system. Authorized personnel, such as system administrators or faculty members, could potentially misuse their access to tamper with or leak sensitive data.
Mitigation: Adopting the principle of least privilege ensures that users are granted access only to the data necessary for their roles. Routine audits, continuous monitoring, and implementing strict access controls can help detect and prevent insider misuse.
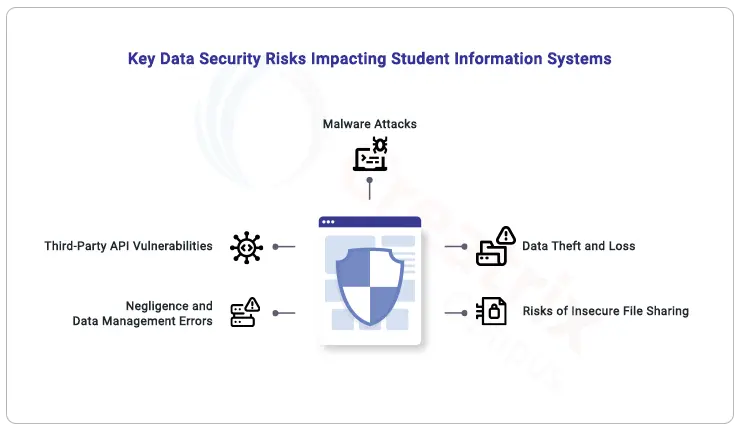
Third-Party Service Providers
Risk: Many institutions rely on third-party service providers for various functions, such as hosting or data processing. If these external vendors do not follow proper security practices, they may expose the ABC system to cyberattacks.
Mitigation: Before integrating any third-party services, institutions must conduct comprehensive security audits and ensure that these vendors comply with robust data protection practices. A formal agreement should outline their responsibilities for data security and confidentiality.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations
Risk: Failure to comply with global data privacy laws can result in legal consequences, financial penalties, and damage to an institution’s reputation.
Mitigation: Institutions must stay up-to-date with relevant data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Personal Data Protection Bill in India, or other applicable laws. Regular compliance checks and data protection training for staff are essential to avoid legal pitfalls.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Why It Matters: Frequent security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities in the ABC system before cybercriminals can exploit them. These proactive steps ensure that the system stays ahead of emerging threats.
Actionable Tip: Institutions should schedule periodic internal and external audits to test the system’s security. Simulated attacks (pen tests) can help reveal weaknesses that need to be addressed immediately.
Ensuring Data Minimization and Retention Policies
Why It Matters: To minimize the risks associated with unnecessary data exposure, institutions should implement data minimization policies. Storing only the necessary data and for only as long as required reduces the surface area for potential breaches.
Actionable Tip: Adopt strict data retention policies that outline the duration for keeping academic records. After this period, sensitive data should be securely deleted or anonymized to ensure it can’t be misused.
Educating Students and Staff on Data Security Best Practices
Why It Matters: One of the most effective ways to mitigate risks is by educating users on how to spot potential security threats and adopt safer online behaviors. Human error is often a leading cause of security breaches.
Actionable Tip: Regularly offer data security training and workshops for students, staff, and faculty. Encourage strong password practices, vigilance against phishing attempts, and responsible sharing of academic information.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Data Security
Why It Matters: Artificial Intelligence (AI) can play a critical role in monitoring and detecting security breaches in real time. AI-driven systems can analyze patterns and alert administrators about unusual activities, often before a breach happens.
Actionable Tip: Institutions should explore the use of AI and machine learning tools to enhance threat detection and response times. AI can also be used to automate security updates and patch vulnerabilities.
FAQs
Final Thoughts
The Academic Bank of Credits system presents an innovative and student-centric approach to higher education, but with the convenience of digital records comes the responsibility to ensure robust data privacy and security.
By adopting the best practices outlined abovesuch as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and thorough vendor assessments educational institutions can safeguard the sensitive data of their students, ensuring a secure, trustworthy system that enhances the academic experience.